Page no: D83
HTTPS: Redirect Configuration in WordPress
How to Redirect: Overview
The main question is how to redirect from HTTP to HTTPS and to force our processes to use HTTPS.
| Object Type | How? | Questions |
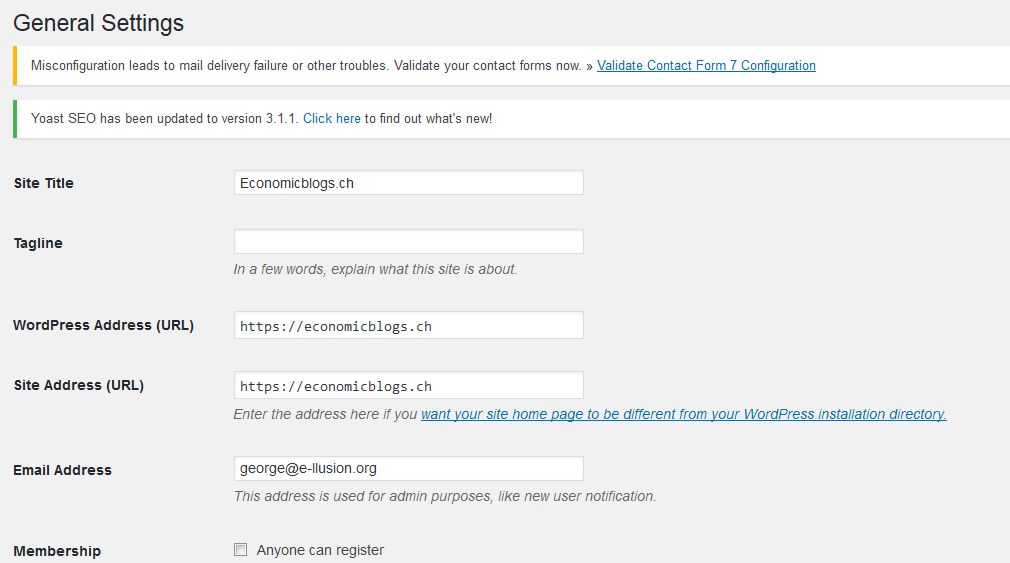
| Homepage | WordPress admin -> Settings -> General | Is this only homepage or also how pages,posts are called from each other? |
| (redirected) domain | no certificate needed | But how do you redirect it? |
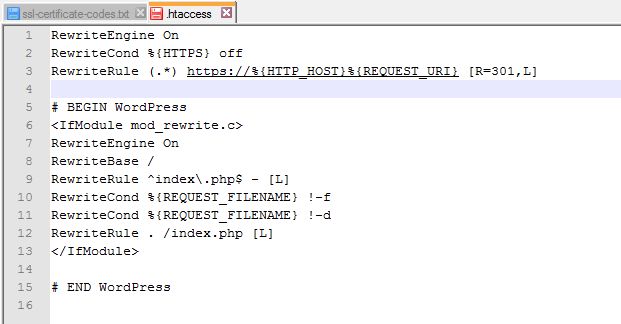
| Pages | Apache Redirect rule in .htaccess NGinx redirect rule on server |
see chapter Technical Background Which ones do we use? |
| Posts | Apache / nginx redirect rule | see chapter Technical Background Which ones do we use? |
| Attachment Page | not documented | |
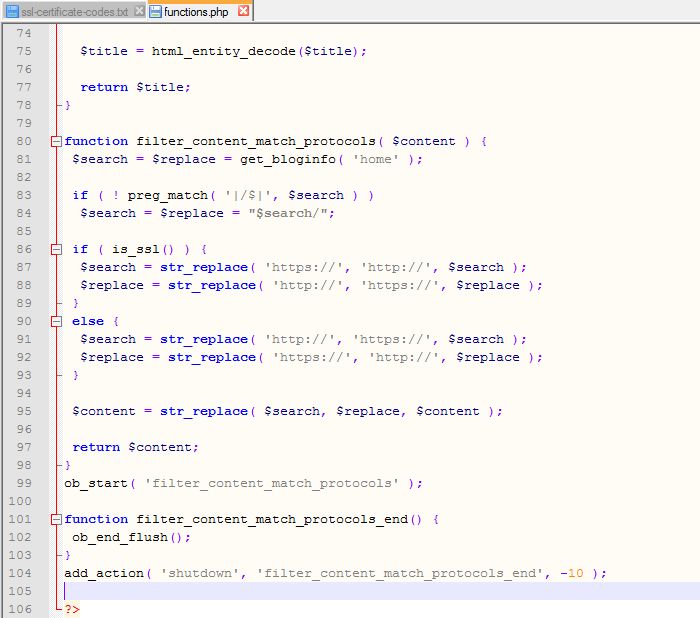
| Media | Custom php filter | not documented |
| Me | ||
| CDN / Cloudfare | Setup it in their GUI | not documented |
| Menu | Change all http URLs to HTPPS | see below |
| Crons | Change executed code in VestaCP | see below |
Redirecting Methods for SSL
SSL Technical Background
Server configuration for SSL
Generally speaking, hosting providers have a service to allow you to enable HTTPS/order a certificate. There are a few types of certificates you can choose from, which differ in a few ways. Every variant also has their own price tag, so before purchasing one, make sure that you go with a certificate that fits your needs and budget!
If you’re a bit strapped for cash and tech-savvy, go take a look at Let’s Encrypt to acquire a free(!) certificate.
If you run and manage your own web server, there are a few things that you’ll have to enable in your server configuration before being able to use SSL certificates. This tutorial explains what steps to take to get a certificate running on your server.
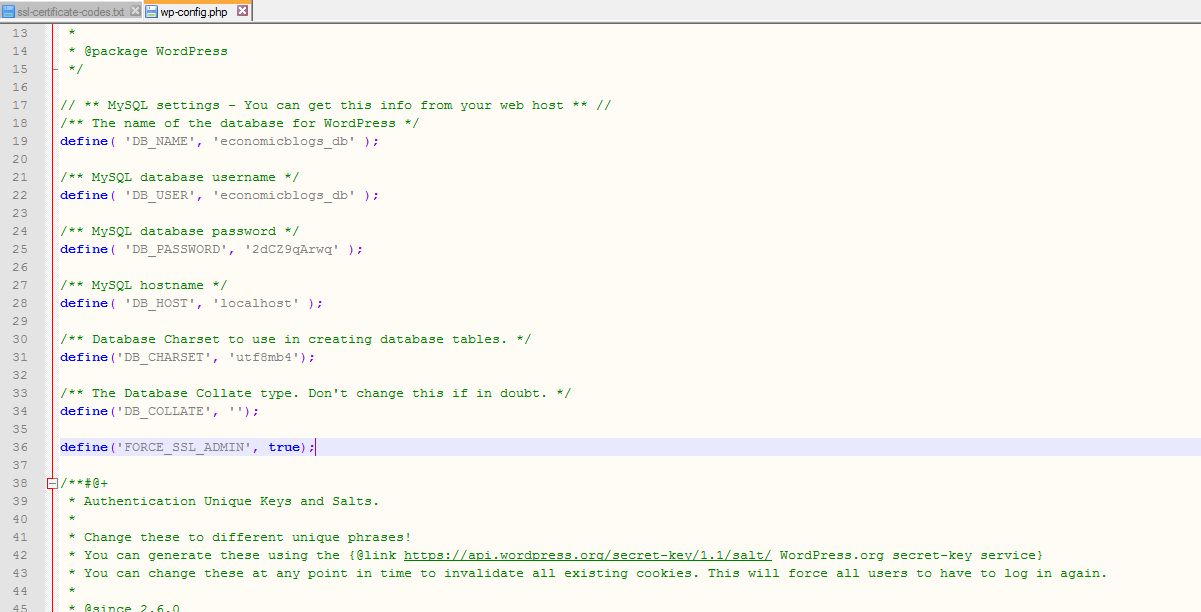
Background: Yoast supports using SSL
OCSP stapling
Having to check the validity of an SSL certificate can result in a small hit in loading speed. To overcome this, you can make use of OCSP stapling. OCSP stapling is a feature that enables the server to download a copy of the certificate vendor’s response when checking the SSL certificate. This means that once a browser connects to the server, it checks the validity of the certificate based on the copy on the server instead of having to query the certificate vendor itself, resulting in a significant performance improvement.
Apache
Before enabling OCSP stapling on your Apache server, please check that you’re running version 2.3.3+ of Apache by running the command apache2 -v (or httpd -v) on your server. Lower versions of Apache do not support this feature.
If you went through the process of setting up HTTPS on your server as described in the ‘Setting up HTTPS & SSL on your server’ section, then you should have come into contact with a VirtualHost configuration specifically made for usage with HTTPS/SSL.
In that file, take the following steps:
- Inside the
<VirtualHost></VirtualHost>section, you should addSSLUseStapling on. - Just above the
<VirtualHost></VirtualHost>section, addSSLStaplingCache shmcb:/tmp/stapling_cache(128000) - Check that the configuration is still valid by running
apachectl -t. If so, reload Apache by runningservice apache2 reload.
After adding these lines to the file, check that the configuration is still valid by running service nginx configtest. If so, reload Nginx by running service nginx reload.
NginxNginx also supports OCSP stapling. Before editing the server configuration, please check that you’re running version 1.3.7+ of Nginx by running the command If you went through the process of setting up HTTPS on your server as described in the ‘Setting up HTTPS & SSL on your server’ section, then you should have come into contact with an Nginx configuration specifically made for usage with HTTPS/SSL. In that file, add the following lines in the
The last line references a file that contains a list of trusted CA certificates. This file is used to verify client certificates when using OCSP. After adding these lines to the file, check that the configuration is still valid by running |
DB Replace
DB Replace is risky, because you can change links, which not must be changed. For example we can change not only the image links, but some scripts or internal/external links. The most disadvantage here is that we can’t easily revert back the changes.
Other issue is that we can mess up the posts from syndication plugin, which will not be easily to track and fix then.
It also will be a problem, if we mess up something and we can’t find the bug at the moment, but after 3 months. We will don’t know for which reason the bug appear and will be needed more time for fixing.
Sometimes on big databases the script can timeout and remove or not save the whole row in the DB, when the MySQL server kills the process. In other words we can lost some data on big db replaces.
See more for